Visual Effects (VFX) is the magical art of creating imagery that enhances or replaces real-world visuals in films, television, video games, and other media. From epic battle scenes in blockbusters to subtle background enhancements in TV dramas, VFX plays a pivotal role in storytelling, captivating audiences, and pushing creative boundaries.
What is VFX?
VFX, or Visual Effects, refers to the integration of live-action footage and generated imagery to create environments, characters, or effects that are otherwise impractical, dangerous, or impossible to film in real life.
Using advanced computer-generated imagery (CGI) and compositing techniques, VFX artists bring fantasy worlds to life, populate scenes with characters, and craft breathtaking visuals that blend seamlessly with live-action shots.
The Role of VFX in Modern Storytelling
VFX has become an indispensable part of storytelling in the entertainment industry. It allows creators to:
- Expand Creative Possibilities: VFX enables filmmakers to craft scenes and settings that are limited only by imagination.
- Create Immersive Experiences: From hyper-realistic environments to lifelike creatures, VFX draws audiences into the story.
- Save Costs: Filming on a digital set or using virtual effects often reduces the cost and complexity of on-location shoots.
- Enhance Narrative Impact: Explosions, natural disasters, and fantastical transformations become believable with VFX, heightening emotional engagement.
How VFX Works: Key Techniques
1. Computer-Generated Imagery (CGI)
CGI is the backbone of modern VFX, creating everything from characters and landscapes to entire virtual worlds. Advanced software like Maya, Blender, and Houdini are used for 3D modeling, texturing, rigging, and rendering.
2. Compositing
Compositing involves combining multiple visual elements into a single cohesive frame. Techniques like green screen (chroma keying) are used to integrate actors into CGI environments or add effects to live-action footage.
3. Motion Capture (MoCap)
MoCap captures the movements of actors to animate digital characters. This technology was crucial in films like Avatar and The Lord of the Rings series, where human performances brought digital creatures to life.
4. Matte Painting
A traditional technique adapted for the digital age, matte painting involves creating realistic digital backgrounds to enhance or replace on-set environments.
5. Simulation Effects
Simulations create natural phenomena like fire, smoke, water, or destruction effects. Software like Houdini is popular for generating these dynamic elements.
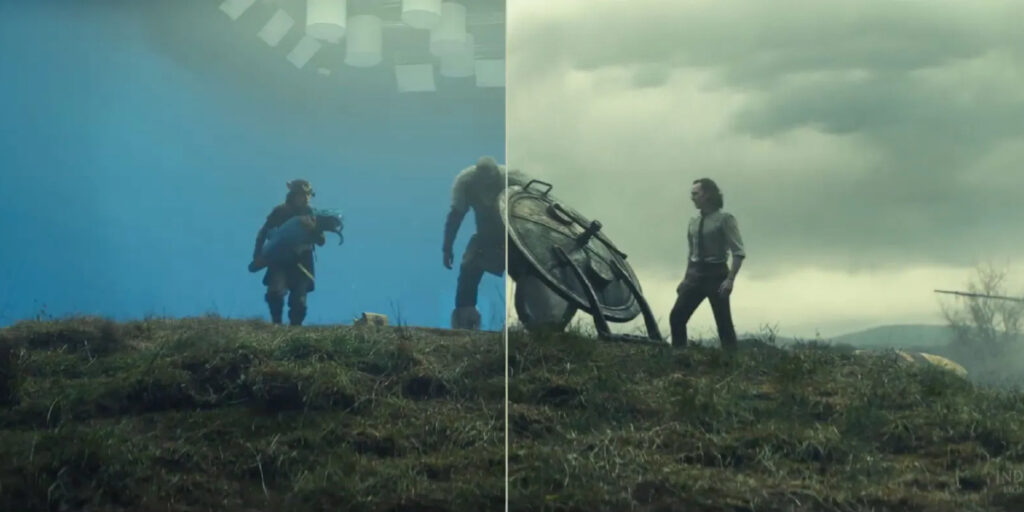

Applications of VFX in Media
1. Film and Television
Movies like Inception, Avengers: Endgame, and Dune showcase groundbreaking VFX. Television series such as Game of Thrones and The Mandalorian also rely heavily on VFX to create vast worlds and realistic creatures.
2. Video Games
VFX enhances gameplay by creating immersive graphics, realistic animations, and engaging environments in games like The Last of Us and Cyberpunk 2077.
3. Advertising and Marketing
Brands use VFX to craft visually stunning commercials that captivate audiences and communicate messages in memorable ways.
4. Virtual and Augmented Reality
VFX is crucial in creating VR and AR experiences, where interactive and immersive environments are key.
The Evolution of VFX
The history of VFX is a testament to human ingenuity. From the use of miniatures and stop-motion animation in early cinema to the groundbreaking CGI in Jurassic Park, the industry has evolved tremendously. Today, VFX relies on artificial intelligence (AI) and real-time rendering technologies to create faster and more realistic visuals.
The rise of virtual production, as seen in The Mandalorian, represents the next big leap. Using LED walls and real-time rendering engines like Unreal Engine, filmmakers can create photorealistic virtual environments directly on set.
Careers in VFX
The VFX industry offers a range of exciting career opportunities for creative and technical professionals. Key roles include:
- VFX Artist: Focuses on compositing, simulations, or 3D modeling.
- Motion Designer: Creates dynamic animations and effects.
- Technical Director: Develops tools and scripts to optimize the production pipeline.
- Matte Painter: Crafts digital backdrops for scenes.
- Motion Capture Specialist: Works with actors and technology to animate digital characters.
With the growing demand for high-quality visuals, skilled VFX professionals are in high demand globally.
Challenges in VFX
Despite its advancements, the VFX industry faces challenges:
- Time-Intensive Processes: Creating high-quality effects can take weeks or months.
- Budget Constraints: Achieving photorealism within budget limits is a constant struggle.
- Burnout in the Industry: The demanding nature of VFX work often leads to long hours for artists.
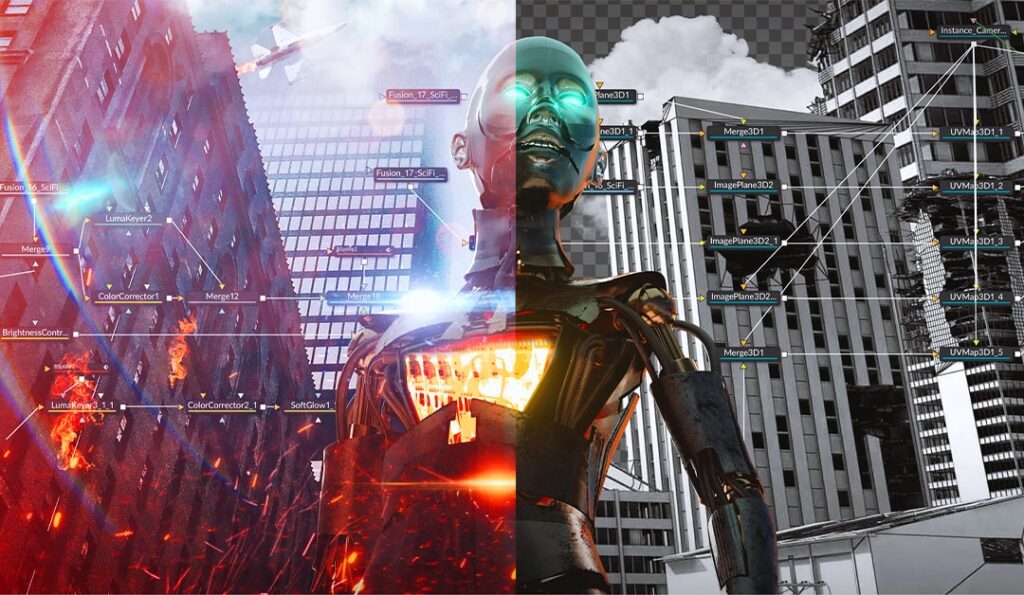

The Future of VFX
As technology continues to evolve, the future of VFX looks brighter than ever. AI and machine learning are streamlining workflows, making it easier to produce high-quality effects faster. Virtual and augmented reality are opening new avenues for immersive storytelling, while advancements in real-time rendering are redefining how movies and games are made.
Conclusion
VFX is a powerful tool that bridges the gap between imagination and reality. From creating fantastical worlds to enhancing everyday scenes, it transforms storytelling across industries. As technology progresses, VFX will continue to push boundaries, inspiring audiences and creators alike.